Fixed Asset Management

Introduction: For any process based manufacturing industry, the input/output ratio depends on the health of the fixed assets. With the type of cost competitive market with paper thin margin, each cost and output aspect are of utmost importance. Fixed assets form a significant portion of its balance sheet. A business can’t manage what it cant measure and this is where Fixed Asset Management comes into play.
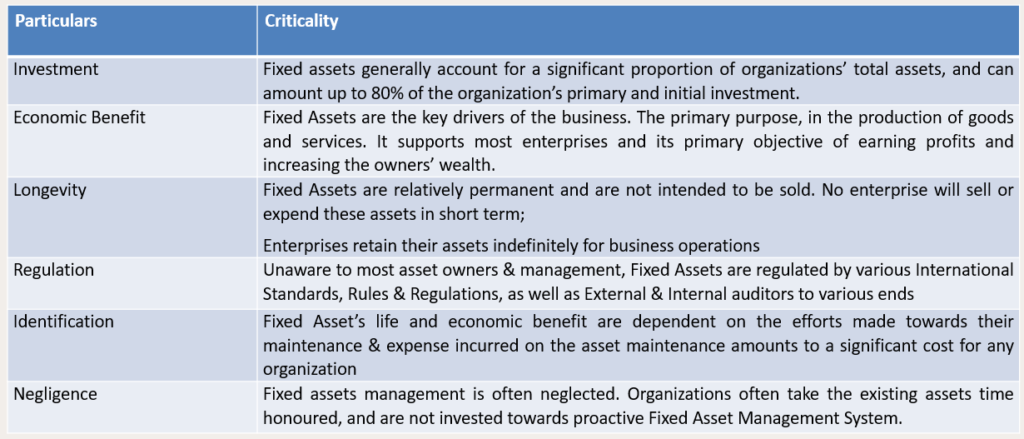
Having inefficient Asset Management leads to following downsides:
QUESTION THE ACCURACY OF FINANCIAL REPORTS: Lack of a strong fixed asset management practice can call the accuracy of financial reports into a question, causing unnecessary turbulence in the finance operations.
MISREPRESENTATION OF FACTS TO STAKEHOLDERS: Inaccurate and in-consistent database often results in misrepresentation of facts. Any records which does not reflect the on-ground position brings the reliability of the same into question.
HIGH ASSET MAINTENANCE COST: Without a robust system to track, evaluate and analyze asset maintenance expenses pattern, multiple avoidable expenses can cause financial drain to working capital of company.
UNDERUTILIZATION / MISUSE OF ASSETS: Production efficiencies are lost on account of underutilization, inefficient maintenance and petty theft of assets.
LACK OF TRAIL: FAM can be seen as a project management that spans over the life of asset, up to 15 – 20 years. Maintaining a trail of 20 years without a system is easier said than done.

Fixed Asset Management System (FAMS)
The traditional methods deployed by businesses for managing their assets and inventory are often outdated as there are multiple inherent challenges faced in Asset Management which call for FAMS. Some of the these challenges are listed below:
INEFFECTIVE CONVENTIONAL METHOD
Management of fixed assets inventory and depreciation schedule using spreadsheets, conducting informal and ad hoc surveys to update its records when the staff has time can lead to gaps in record keeping, quickly throwing the inventory management off track.
LIMITED IN-HOUSE RESOURCES
The luxury of time and expertise is something not every organization might have. Considering the time allocation, the finance resource faces with their day to day operation, they might not have the adequate time to be invested in the improvement of the existing process.
HIGH OPPORTUNITY COST
Besides asset management, the team is already pre-occupied with other critical tasks, and the trade off of time required to manage fixed assets that they could otherwise devote to higher value projects at the company has a very high opportunity cost.
GEOGRAPHICALLY & DEPARTMENTALLY SEGREGATED ASSET BASE
Finance staff may have to partner with other areas such as the IT / Admin department or regional offices, which may have their own records of the fixed assets, and the process of reconciling multiple sets of records adds an extra administrative burden for everyone involved.
LACK OF AUTOMATION
Manually managing fixed assets consumes a considerable amount of time. In fact, it’s one of the most common productivity drains that plague growing businesses. On an average, a company requires a full time resource to manage its growing assets
FAMS becomes critical on account of multiple reasons owing to higher stakes attributable to a company’s fixed asset function:
Benefits
At the inception of any business, the size of operations is small with few assets & limited manpower. At this stage, all significant transactions are taken care by a limited resources and managing the business becomes relatively an easy task. However, as the business starts growing, the trajectory and volume also Starts increasing in same proportion. Diversification , expansion and cross border transactions have added complexities in business and thus the management function has also grown equally vast and complex. Therefore, it becomes critical for an entity’s success to properly track assets, regardless of size of an organisation. Fixed assets are defined as any ‘permanent’ object that a business uses internally including but not limited to computers, tools, software, or office equipment.
While employees may utilise a specific tool or tools, the asset ultimately belongs to the company and must be returned. And therefore without an accurate method of keeping track of these assets it would be very easy for a company to lose control of them
- Fixed Assets Management System is a subsystem of the entity’s management system, focusing on Fixed Assets.
- Understanding and knowing the assets owned by the company, described as the Assets Health Report Card.
- Illuminating information concerning the company assets enabling decision-making for future investments pool.
- Contributing an effective control & monitoring system over the assets, uniformity across the departments and functions of the company.
- A system of methods, policies, and procedures addressing the acquisition, use, control, protection, maintenance, and disposal of assets.
- Accuracy on asset control, monitoring the future and the past records outlining the details associated to the asset concerned.
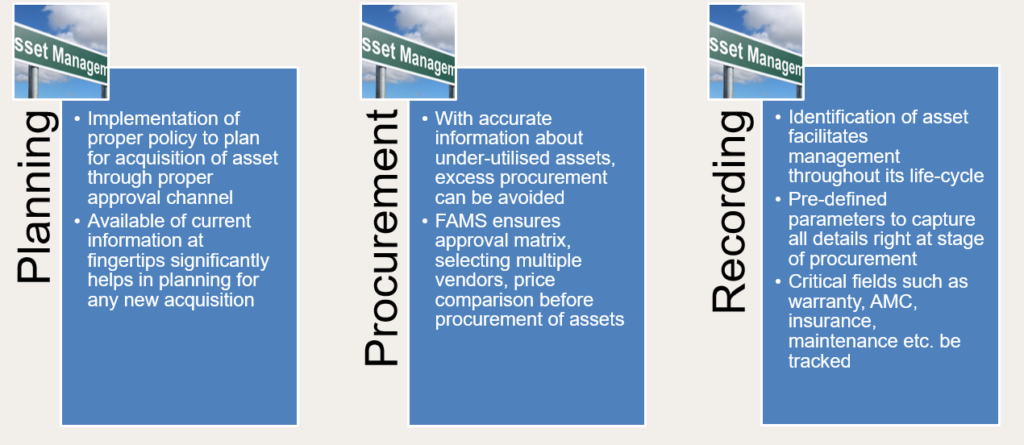
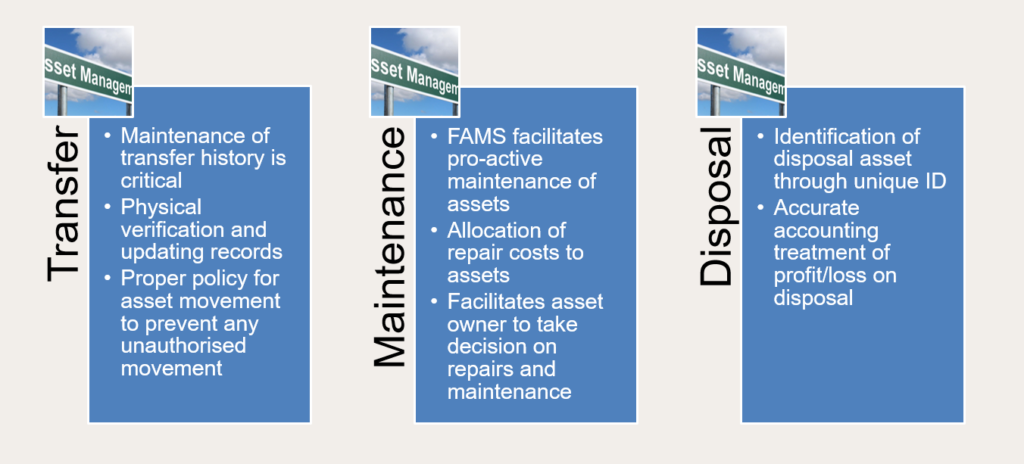
Life Cycle
Approach
NDM has proven track record providing end to end FAMS and allied solutions to help businesses overcome the challenges posed by fixed asset management:
COMPONENT LEVEL FIXED ASSET RECORD
Preparation of Fixed Assets Register at a component level, where each asset is reflected independently with all its relevant parameters with including its calculated depreciation details.
CENTRALIZED DATABASE OF ASSET, IDENTIFYING EACH ASSET ON GROUND
A centralized database of all assets with 3 level location details available on the fingertips of the management, which in turn enables the management to identify each asset on floor.
IDENTIFICATION AND RECONCILIATION OF GAPS – PLOT TO EXECUTION
Any discrepancy in books in terms of any surplus or shortage of assets on floor can be identified and reported to the management and accounted in books for transparency.
AUTOMATION
The entire Fixed Assets Lifecycle management process can be automated significantly reducing manual process and physical documents involved and minimizing the time required.
AFTER SALES SUPPORT AND ANNUAL MAINTENANCE
Our support does not end with first time implementation of FAMS. We provide our continuous support to the organizations to better improve their process and other regular consultancy including audit support, updating FAR and tagging support.
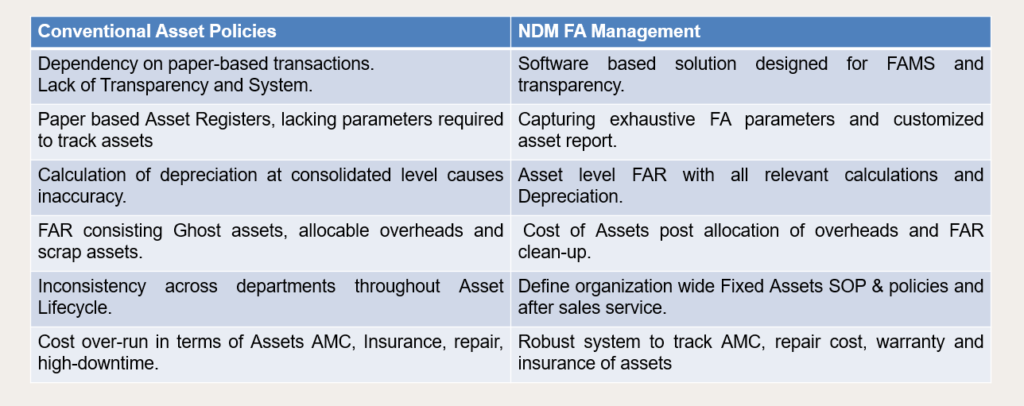
NDM works closely with businesses to create a constructive and progressive FAMS framework. Following are the critical variances we endeavour to create:
At NDM, we follow scientific approach to FAMS customised to the specific needs of business and our methodology includes the following:
STEP 1- CAPITAL TRANSATION ANALYSIS
In this stage, we analyze the existing records of capital expenditure with the company. Existing records can be in way of accounting software (Tally / ERP), physical files, departmental database / checklists or any other similar records.
- Componentization: Based on the existing records, we prepare an asset level details with Financial parameters such as vendor details, PO and invoice details, date of purchase / capitalization etc
- ABC Analysis: We perform a critical analysis of the assets and then identify high priority assets placed in the organization. The management may set better internal control and management policies for the same.
- Fictional Assets: Fictitious assets are the expenses which are not fully written off. Often, these expenses end up in FAR. We identify the same and take appropriate calls to adjust same in books
- Incidental Expenses: In addition to the asset purchase price, many incidental expenses (freight, taxes, insurance, labor charges) are incurred, which should be grossed up with the original asset in books
STEP 2- ASSET LISTING
In this stage, a complete wall-to-wall physical verification of assets is conducted covering all locations, and an exhaustive list of assets as on date is obtained. Various asset parameters required for documentation is also compiled for each asset.
- Physical Verification: A complete wall-to-wall verification covering all the assets owned by the company. This lets us weed out any fictional assets which are not physically present for use
- Assets Parameters: We capture various assets parameters including asset make, model, serial number, working status. Additionally, details such as location, department, custodian etc. are also captured
- Consolidated List: Assets listing provides company’s consolidated list of assets. Since this is an independent activity, any assets owned by the company not appearing on books are also brought on records
- Transparency: Since we provide a location wise asset database, it enables the management perform analysis on adequacy of asset. Management can identify whether an asset is lacking/surplus at any location
STEP 3- ASSET LABELLING
In this stage, each asset is provided a unique identification code in form of Bar-coded / QR coded tags. Varieties of tag materials with economic and high security options can be used depending on the class of assets.
- Unique ID: A bar-coded / QR coded tag is affixed to each asset. This code acts as a unique ID for each asset which can be used to track throughout various stages of its lifecycle.
- Automation: Barcodes and scanners introduces automation in physical verification. The tags can be quickly scanned to record the verification and record any remarks for each asset
- Customised Tags: Custom size, design and materials are available as per the requirement of the company. Tag options ranges from paper, polyester, metal, acrylic to high end RFID and Geo Tags
- Internal Controls: Affixing asset tag to an asset establishes traceability for the asset, and thus increases the internal controls. The fact that the asset is being tracked acts as a theft or otherwise misuse deterrent.
STEP 4- FINANCIAL RECONCILIATION
In this stage, we perform reconciliation between the assets captured from our Physical Verification stage with the records available with the company. Gaps in form of Ghost Assets or surplus assets are identified and treated accordingly
- Ghost Assets: Ghost asset is an asset in books that cannot be accounted for because it is physically missing or otherwise rendered unusable. Such assets should be identified and removed from FAR.
- Surplus Assets: Surplus assets refers to those assets which are owned by the company, and are in use, but for various reason not recorded in books. Such assets needs to be added in FAR.
- Allocation of Expenses: All the allocable incidental expenses identified during financials analysis are appropriately allocated to the respective asset and accurate historical cost of asset reported.
- Cost Centre accounting: To appropriately ascertain cost center wise profit, each asset can categorized to cost center to calculate and allocate depreciation to corresponding cost centre.
STEP 5- REPORTING
In this stage, we prepare a project report and other deliverables. In addition to a component level Fixed Assets Register, we also report identified gaps, prepare an organization wide Standard Operating Procedure and any other policy documents
- Fixed Assets Register: Component level Fixed Asset Register with complete particulars of assets, and its various financial and physical parameters along with project report is our foremost deliverable.
- Gaps Reporting: Any discrepancies and otherwise observation, identified during the project including gaps in internal control is also compiled and reported to the management.
- SOP: Any policy is only effective if it is followed consistently and uniformly by all locations and departments, and SOP helps ensures that throughout the organization
- Policies: Along with reporting, we assist management in identification of any area classifying under weak internal controls, and draft some of the best industry practices / policies to overcome such weakness.
STEP 6- AUTOMATION
This is where your Fixed Assets Management Solutions actually takes off. You will be able to transfer the existing process of asset management to new height with the use of smart-phone, custom software and other tools to streamline automation
- Custom Software: The custom software is designed for FAMS. Its various modules such as depreciation, maintenance, transfer and audit module brings a technical edge to your asset management need.
- Integration: FAM software can be fully integrated with your existing organization ecosystem, thereby providing a seamless experience to the operating staff & management.
- Updates: FAM software are regularly updated and improved to further automate and streamline asset management. These updates are available as a part of FAM Software AMC.
- Smartphone Integration: FAM Software helps bring your Android / iOS smartphones as an asset management tool. You can easily view and manage assets using the smartphones and FAM Software
STEP 7- UPDATES
We strive for customer satisfaction, and to ensure that we remain in constant touch base with the client team to provide Annual Maintenance Services and after sales support services
- Audit: Post implementation of FAM, our team also co-ordinates with your team to conduct Fixed Asset Management Audit and other policy audit to ensure policies are being followed properly.
- Updating FAR: We also provide required consultancy services to the organizations on monthly / quarterly / semi-annually / annually basis to ensure that the Fixed Assets Register are being
- User Training: We remain in constant touch base with the client team responsible for operating the FAM software, and takes care of user training issues to ensure your software runs without snag.
- Consultancy: Even after implementation, we remain in contact with the management for any consultancy services required in the field of asset management or otherwise to ensure continued support
Related Post
Have Any Question?
Send us a message and tell us more about your business and financial goals. We will get back to you soon to schedule a consultation.